
The first is usually taught in middle school science. The body has two ways to create more cells. This has to do with how they replicate themselves. To recap, we have certain types of stem cells that can become a variety of different cells-they are like the renaissance men of cells-but there is one more thing that makes stem cells special. Another example is mesenchymal (meh-sen-ki-mal) stem cells, which can be found in the umbilical cord tissue and can become a host of cells including those found in your nervous system, sensory organs, circulatory tissues, skin, bone, cartilage, and more. Hematopoietic stem cells (Greek “to make blood” and pronounced he-mah-toe-po-ee-tic) found in the umbilical cord's blood, for instance, can become any of the different types of blood cells found in the body and are the foundation of our immune systems. (Later, we will learn why not all adult stem cells are equal.) Adult stem cells are more limited in the types of cells they can become, something known as being tissue-specific, but share many of the same qualities. These stem cells, known as adult stem cells, stay with us for life. Thankfully, we can also acquire stem cells that form just a little bit later down the road, like in the umbillical cord. These early stage stem cells are master cells that have the potential to become any type of cell in the body.įirst isolated in 1998, there is a lot of controversy around acquiring embryonic stem cells. These completely undifferentiated cells can be found during gestation, or the time the baby is in the womb, and are called embryonic stem cells.
#ADULT STEM CELLS HOW TO#
Your cells didn’t start out knowing how to come together to form your bones, heart or blood they begun with more of a blank slate. Researchers are currently conducting clinical trials with stem cells, adding to the growing list of 80 diseases which they can treat. The relatively recent discovery of stem cells in the umbilical cord's blood has proven advantageous over acquiring stem cells from other sources. The discovery of certain markers allows us to see how compatible a donor’s and host’s cells will be. Although a person’s own stem cells are always 100 percent compatible, there are risks in using someone else’s stem cells, especially if the donor and recipient are not immediately related. It wasn’t until we found out where and how to isolate these cells that we started using them for transplants.
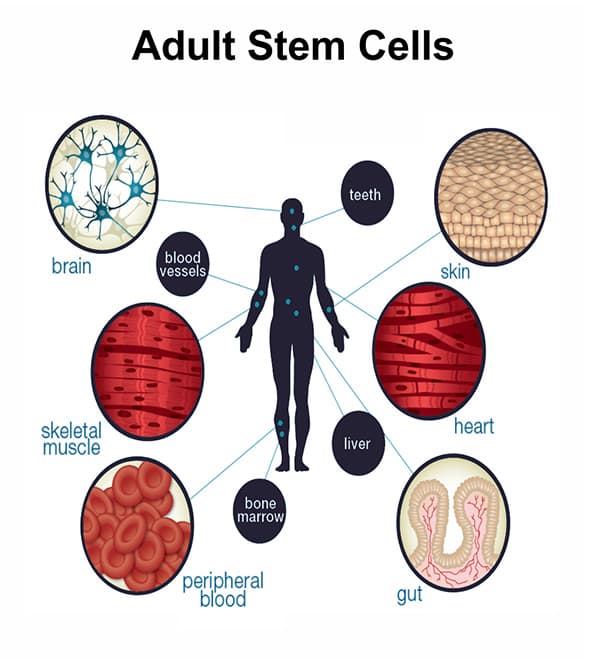
Stem cells play a huge part in the body’s healing process, and the introduction of new stem cells has always showed great promise in the treatment of many conditions.

Stem cells are unique cells: They have the ability to become many different types of cells, and they can replicate rapidly. A stem cell has the potential to become one of many different types of cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
